
Birth the process of transitioning the baby from the fluid environment to the real world where we need air to breathe. Usually, babies experience breathing difficulties after birth, and that is during the first few hours after coming out from her mother’s womb. But there are complex breathing problems that you should be aware of and be cautious.
Asphyxia
It rarely happens that a newborn baby may have no or poor breathing because of insufficient oxygen due to complications during labor, delivery or after birth. When a newborn baby is running out of oxygen, the breathing becomes fast and shallow. In the worst-case scenario, if the baby stops breathing, the heart will fail to function and lose muscle strength.
But the baby can still be revived by merely exposing her to oxygen, but an indication of oxygen insufficiency happens again, the baby stops to breathe again. There will be dropping of heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle tone and ultimately die unless an immediate resuscitation will be executed. At this point, there is a high risk that the brain will slowly damage because of the low oxygen that reaches the brain.
The immediate response of doctors and nurses
- Minimize the heat loss: The baby will be sited in a warmer to prevent the loss of heat and drying of any amniotic fluid
- Execution of mouth and nose suction: The health-care providers will conduct the suction of the baby’s mouth and nose
- Immediate examination: The newborn baby will undergo an in-depth examination to test the breathing, heart rate, and color. The examination will rapid and shall be done in less than 20 seconds
- Ventilation: A bag and mask will be used to give ventilation to the baby. There is a constant checking of the heart rate every few seconds. The doctor will continue the ventilation procedure if the baby still responds to a low and decreasing heart rate. The doctor will also start executing the baby chest compressions when necessary
Read also: Colic and how to deal with it
- Intubation: If ventilation does not work, a tube will be inserted into the baby’s windpipe. The tube will give a gentle puff of air in a rate of one breath for every one second. In most cases, intubation as a last resort works effectively to revive the baby
- Chest compressions: The doctor will give a press on the baby’s chest three times every two seconds, and the ventilation bag will be used to provide air. The doctor will continuously check the heart rate every half a minute. If needed, the doctor will give chemical resuscitation
- Medicines: if necessary, during continuous resuscitation, epinephrine will be given by IV or through the tube. It can increase the heart rate and improve the blood flow of the baby
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
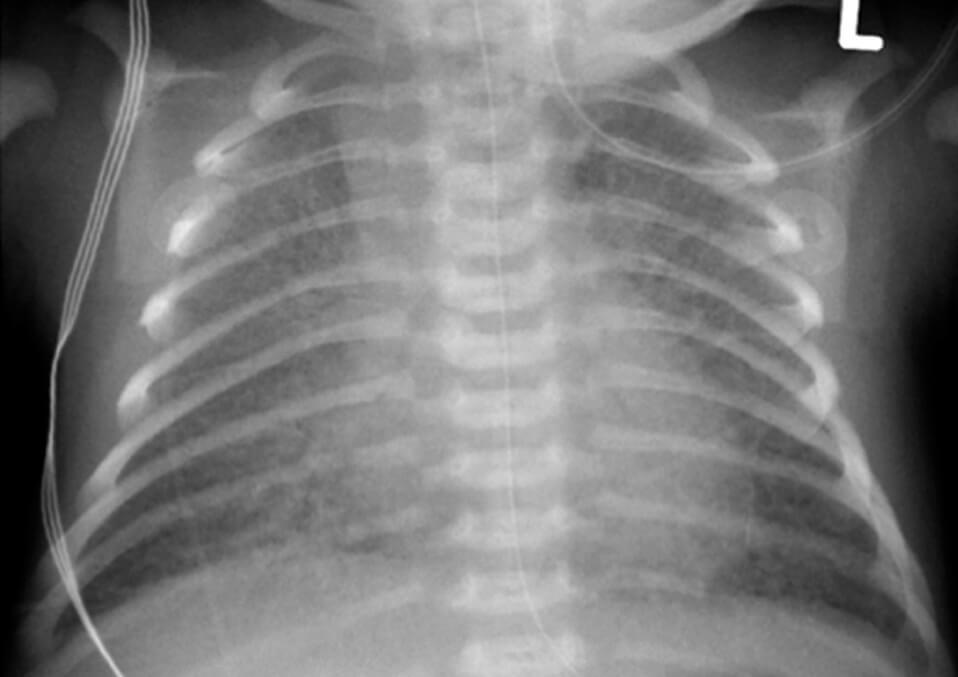
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) is a state where after birth, the breathing is rapid for a short period. It is also known as ‘wet lung’ that will have the following indications:
- Retractions: It is the inward movement of the muscles underneath the rib cage
- cyanosis: a bluish mark of the gums, lips, and skin
When the baby was still in the mother’s womb, the baby’s lungs are expanded with fluid. During birth, the fluid must be gone and replaced by air. The fluid is removed by the birthing process itself. The rest of the fluid is gone through the lymph system and blood vessels. TTN happens if the fluid is not immediately removed. Babies that are born through cesarean have a higher risk of TTN.
Read also: Frequent and severe crying of babies
TTN is distinguished by examining the symptoms, signs, and x-rays. Typically, the symptoms are treated with little extra oxygen only. Then an introduction of antibiotics is done for the first two days. In most cases, newborn babies can immediately recover from TTN in three days.
How the surfactant works
A surfactant is a substance that functions to keep the alveoli open. Surfactant is foamy, the fatty liquid that functions as a grease. The air sacs will have the difficulty of functioning if there is no surfactant. It allows the air sacs to remain open.
The surfactant develops at the 24th week of pregnancy and achieves its full development up to the 35th week. During labor, the mother’s body will naturally produce steroid that will pass through the placenta and umbilical cord and initiates the production of surfactant to the lungs of the baby. If babies do not have enough surfactant, then they will be vulnerable to respiratory distress syndrome.
Read also: Lip tied babies and what you should do
If the delivery is through cesarean, the mother will be given steroids to help the fast production of the surfactant to the baby’s lungs. If the case is premature birth, the introduction of steroids will not be appropriate. Instead, the doctor will administer artificial surfactant. The ultimate goal is to make the baby’s breathing stabilize and become healthy. Sometimes, the doctor will provide supplemental oxygen or through the ventilator.
Indeed a vast percentage of newborn babies that recover from respiratory distress syndrome show no significant complications as they grow older. However, for babies the experience severe respiratory distress syndrome, especially those born prematurely are having the risk of difficulty in breathing. It includes chronic lung illness and respiratory problems.
Read also:
- Baby’s Breathing Problems
- How Many Weeks is a Normal Pregnancy?
- All of the Things you Need to Know About Nut Allergy During Pregnancy


